The composite technology of rubber and ceramics has demonstrated unique advantages in the industrial field by combining the flexibility of rubber with the high wear resistance of ceramics. This article systematically introduces the technical characteristics and market applications of three types of products, namely wear-resistant ceramic-rubber composite plates, from the perspectives of material properties, application scenarios and technological innovation.
1. Wear-resistant ceramic rubber composite plate
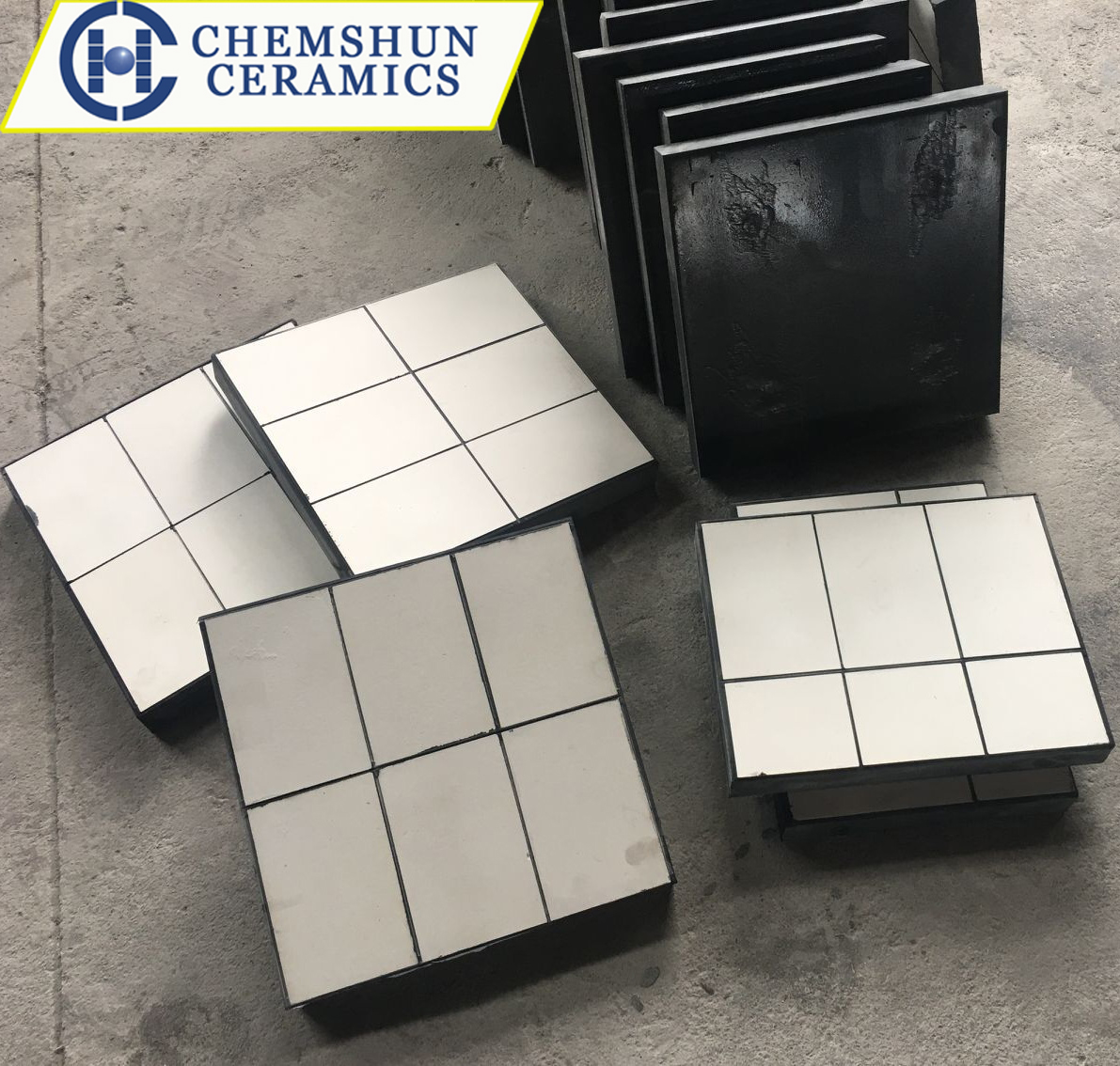
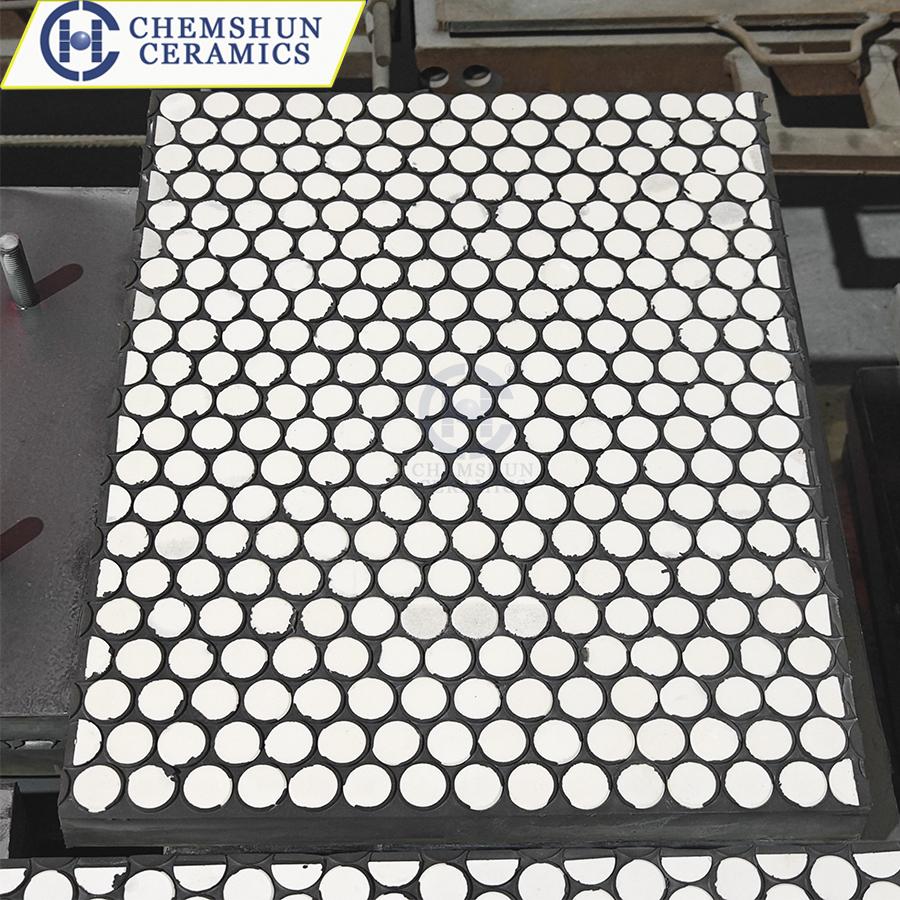
By embedding ceramic sheets into the rubber matrix, wear-resistant ceramic-rubber composite plates with both impact resistance and wear resistance are formed, which are widely used in high-wear environments.
2. Structure and Process
①Two-in-one structure: Ceramic sheets (such as alumina or ZTA ceramics) are embedded in special rubber and fixed through vulcanization process to form a flexible anti-wear layer. Ceramic plates are mostly designed in square or circular shapes, which can effectively decompose the impact force of materials.
②Three-in-one structure: By adding a steel plate layer on the basis of ceramic and rubber, it further enhances mechanical strength and is suitable for scenarios that require welding or bolt fixation (such as hoppers and drop chutes).
③Manufacturing process: Ceramic sheets are fired at high temperatures in a tunnel kiln, combined with nitrile rubber vulcanization technology to ensure high-strength bonding between ceramics and rubber. At the same time, it has passed the ASTM65 wear resistance test.
3. Performance advantages
①Impact resistance: The rubber matrix absorbs impact energy, preventing ceramic fragmentation, and is suitable for high-drop transportation scenarios such as ores and pulp.
②Lightweight and corrosion resistance: Its density is only 30% of that of steel plates, and the ceramic surface does not stick to materials and is corrosion-resistant, reducing the frequency of equipment maintenance.
③Construction flexibility: It can be cut into irregular structures to meet the inner lining requirements of complex equipment. After installation, there is no gap, effectively preventing material blockage.
4. Application
It is mainly used in high-wear scenarios such as coal conveying systems in thermal power plants, silos in the metallurgical industry, and steel sintering plants, with a temperature adaptability range of -40℃ to 100℃.
Post time: May-21-2025